As the global economic landscape presents a potential recession and inflationary pressures, Information Technology (IT) departments are exploring cost-effective strategies that maintain critical operations. A prevalent solution emerging is cloud storage tiering.
The constant surge in data generation has led to a steady increase in storage costs, with annual expenditure per terabyte exceeding $3,000. According to expert analysis, storage and storage management costs can consume up to a third of an organization’s IT budget. A recent survey indicates that over half of businesses find their current data storage expenses untenable.
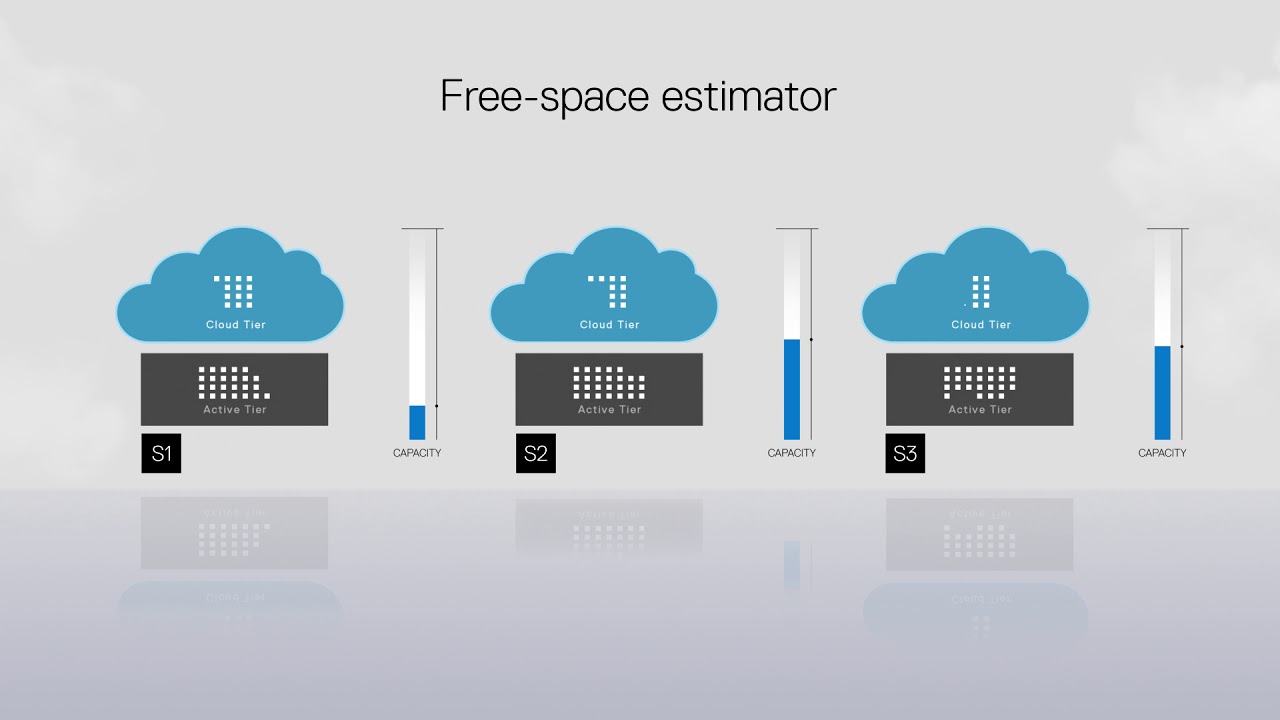
Cloud tiering is a strategic approach to optimizing storage expenditure by integrating economical cloud storage with pricier local storage hardware. The principle is to classify data according to its business value. “Hot” data, which requires immediate access for applications, is stored on high-performing, costly local tiers such as flash memory or solid-state drives. Conversely, “cold” data used for archives and backups is relocated to cheaper, high-capacity cloud tiers.
Automated Management Tools for Tiering
Storage management software tools can implement tiering, allowing organizations to establish policies for data movement between tiers based on preset criteria. These tools perform an analysis of data usage patterns, file types, and other associated metadata.
When cold data is identified, it is automatically transferred to cloud storage services such as Azure Blob storage, AWS S3, or Google Cloud Storage. These cloud object storage options are approximately 40 times cheaper than local storage alternatives, making them the preferred choice for storing snapshots, logs, backups, and archives. As cold data is infrequently accessed, companies can reduce data egress fees charged by cloud providers for data retrieval.
Cloud tiering not only provides cost advantages but also significantly enhances performance. Most organizations depend on certain mission-critical applications that cannot withstand storage latency. Storing hot data on high-performance tiers ensures swift access to frequently used data, minimizing latency and enhancing application performance.
Scalability and Compliance through Cloud Tiering
Cloud tiering also promotes scalability. The ability to seamlessly move data between different tiers based on changing needs enables organizations to adjust their storage capacity without substantial infrastructure modifications.
Moreover, cloud tiering bolsters compliance efforts. Regulations like Sarbanes-Oxley, HIPAA, and the EU General Data Protection Regulation mandate organizations to retain specific data types for extended periods. By leveraging a cloud storage tier, organizations can automate data retention and deletion in accordance with policies designed to meet long-term retention requirements. Cloud tiering also facilitates compliance with regulations necessitating data encryption both at rest and in transit.
Cloud tiering further aids disaster recovery. Data replication across different storage tiers in diverse geographical locations ensures data availability in case of disasters or unexpected events.
The Role of Intelligent Tiering Services
Intelligent tiering services are an integral part of modern cloud storage solutions. They bring an additional layer of automation to the data storage process, effectively reducing manual intervention and optimizing costs. Services such as AWS’s S3 Intelligent-Tiering, Google Cloud’s Cloud Storage, or Azure’s Blob Storage, employ machine learning and predictive analytics to monitor data access patterns and automatically move data between different storage tiers.
These services are designed to address the issue of data lifecycle management, which can be complex and time-consuming. By using intelligent tiering services, organizations can ensure that their data is stored cost-effectively, without compromising performance or accessibility. This is particularly valuable for data with unknown or changing access patterns.
Moreover, these services often come with built-in features to handle data archival and long-term backup. They can automatically transition data to even lower-cost storage tiers if it hasn’t been accessed for a certain period of time. This further helps organizations in managing their data storage costs and adhering to various data retention policies and regulations.
In the face of exponential data growth, organizations are compelled to seek cost-efficient alternatives to traditional on-premises storage and data management solutions.
Cloud tiering addresses these concerns by shifting cold data to the cloud, ensuring easy accessibility without squandering high-performance, costly in-house storage hardware.